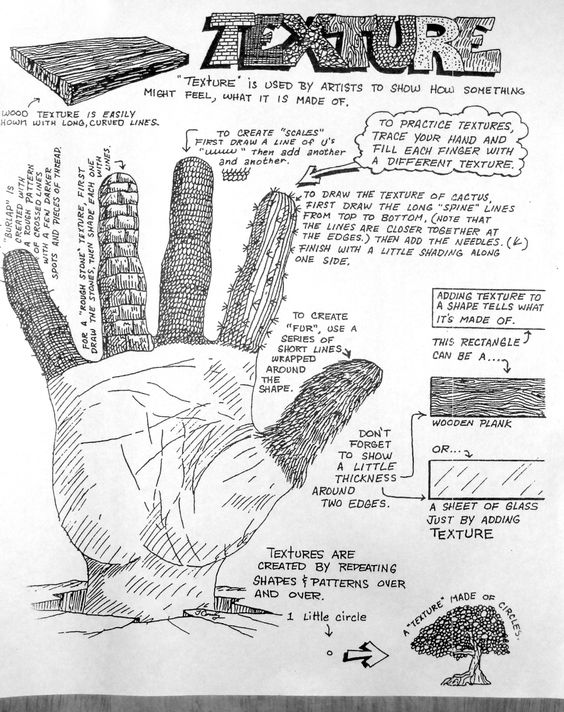
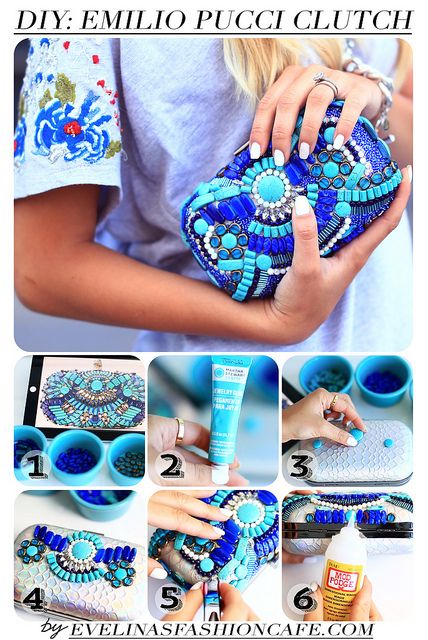
Texture (Activity)
Make no longer used clutch, purse, pouch, pencil case, hand phone case, etc into new one by making the surface have texture!



Quiz (Kahoot & ProProfs Quiz)
Week 11 Classroom Resources: Video
Define the meaning of aperture, shutter speed, ISO and DOF
Aperture : a hole or small opening in something. : an opening that controls the amount of light that passes through a lens (such as a camera lens)
Shutter speed: Shutter speed is the unit of measurement which determines how long shutter remains open as the picture is taken. The slower the shutter speed, the longer the exposure time.
ISO : In Digital Photography ISO measures the sensitivity of the image sensor. The same principles apply as in film photography – the lower the number the less sensitive your camera is to light and the finer the grain.
DOF : Also called focus range or effective focus range, is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image.
Differentiate the purpose of camera angles and shots.
Camera angle also include the eye-level camera angle and the point of view shot. A high-angle shot (HA) is a shot in which the camera is physically higher than the subject and is looking down upon the subject.
Camera Shots. A camera shot is the amount of space that is seen in one shot or frame. Camera shots are used to demonstrate different aspects of a film’s setting, characters and themes. As a result, camera shots are very important in shaping meaning in a film.
Week 10 Classroom Resources: Audio
List format audio
- PCM
- WAV
- AIFF
- MP3
Differentiate lossy and loseless.
Lossless and lossy compression are terms that describe whether or not, in the compression of a file, all original data can be recovered when the file is uncompressed. With lossless compression, every single bit of data that was originally in the file remains after the file is uncompressed. Lossy compression is generally used for video and sound, where a certain amount of information loss will not be detected by most users.
Week 6 Media and methods of Instructions
Compare and contrast teacher vs student centred learning strategies.
In teacher-centered education, students put all of their focus on the teacher. You talk, and the students exclusively listen. During activities, students work alone, and collaboration is discouraged.
Pros
- When education is teacher-centered, the classroom remains orderly. Students are quiet, and you retain full control of the classroom and its activities.
- Because students learn on their own, they learn independence and make their own decisions.
- Because you direct all classroom activities, you don’t have to worry that students will miss an important topic.
Cons
- When students work alone, they don’t learn to collaborate with other students, and their communication skills may suffer.
- Teacher-centered instruction can be boring for students. Their minds may wander, and they may miss important facts.
- Teacher-centered instruction doesn’t allow students to express themselves, ask questions, and direct their own learning.
When a classroom operates with student-centered instruction, students and instructors share the focus. Instead of listening to the teacher exclusively, students and teachers interact equally. Group work is encouraged, and students learn to collaborate and communicate with one another.
Pros
- Students learn important communicative and collaborative skills through group work.
- Students learn to direct their own learning, ask questions, and complete tasks independently.
- Students are more interested in learning activities when they can interact with one another and participate actively.
Cons
- Because students are talking, classrooms may often be noisy or chaotic.
- Teachers may have to attempt to manage all students’ activities at once, which can be difficult when students are working on different stages of the same project.
- Because the teacher doesn’t always deliver instruction to all students at once, some students may miss important facts.
- Some students prefer to work alone, so group work can become problematic.
Compare and contrast the advantages and limitation of
a. Cooperative learning
b. Gamification
c. Discovery learning
d. Inquiry-based learning
e. Project/Problem based learning
| ASPECT | ADVANTAGES | LIMITATIONS | ||||||||
| Cooperative Learning | Students learn to relate to their peers and other learners as they work together in group enterprises. This can be especially helpful for students who have difficulty with social skills. | Yet students need to have experience with working in groups if for nothing else to develop the generic skills required by industry. For that reason alone lecturers need to provide collaborative learning opportunities, which means understanding the various approaches, their disadvantages and their issues. | ||||||||
| Gamification | Gamification in eLearning provides an effective, informal learning environment, and helps learners practice real-life situations and challenges in a safe environment. | Gamification is not useful for making people work harder, but it can be used to encourage people to work better. | ||||||||
| Discovery Learning | Discovery learning has many key advantages, such as it can be adjusted to the learner’s pace. It promotes autonomy and independence. It ensures higher levels of retention |
|
||||||||
| Inquiry -Base Learning | When children learn science through inquiry, they communicate their thoughts and ideas through practical action as well as through symbols (speech, writing, numbers, drawings). It also gives teachers direct knowledge of the child’s capacity to successfully carry out inquiry. | It makes high demand on the students as well as teachers | ||||||||
| Project/Problem based Learning[ | PBL encourages learning from experience, allowing students to use and organize what has been learnt to understand problems | · Difficult with large class
· Different type of students (quiet students – dominant students) |
Week 5 : Instructional System Design: Theory and Model
Define cyberlearning with example of classroom application.
The term “cyberlearning” reflects a growing national interest in managing the interactions of technology and education, especially with respect to the use of networking and information technologies. Example :
1. Classroom as Virtual Phenomenon: RoomQuakes and WallScopes
2. Games for Good: Learning While You Play
3. Teaching Tykes to Program: Never Too Young to Control a Robot
4. Virtual role-play and robo-tutors
5. Tools for Real-time Visual Collaboration
6. Fusing data collection, computational modeling and data analysis
7. Virtual Worlds and Augmented Reality: Increasing ecological understanding
Describe cyberlearing literacy and its implementation in classroom.
It requires critical thinking skills, an awareness of the necessary standards of behaviour expected in online environments, and an understanding of the shared social issues created by digital technologies.
Identify three web 2.0 resources.
Web 2.0 tools are online software programs that allow users to do a number of different things. They can be used to teach curriculum content, store data, create or edit video, edit photos, collaborate and so much more. These programs are often free and are used by teachers, students and sometimes parents, both in and out of the classroom, on a pretty regular basis.
1. Pinterest
2. Edcanvas
3. Powtoon
LESSON PLAN
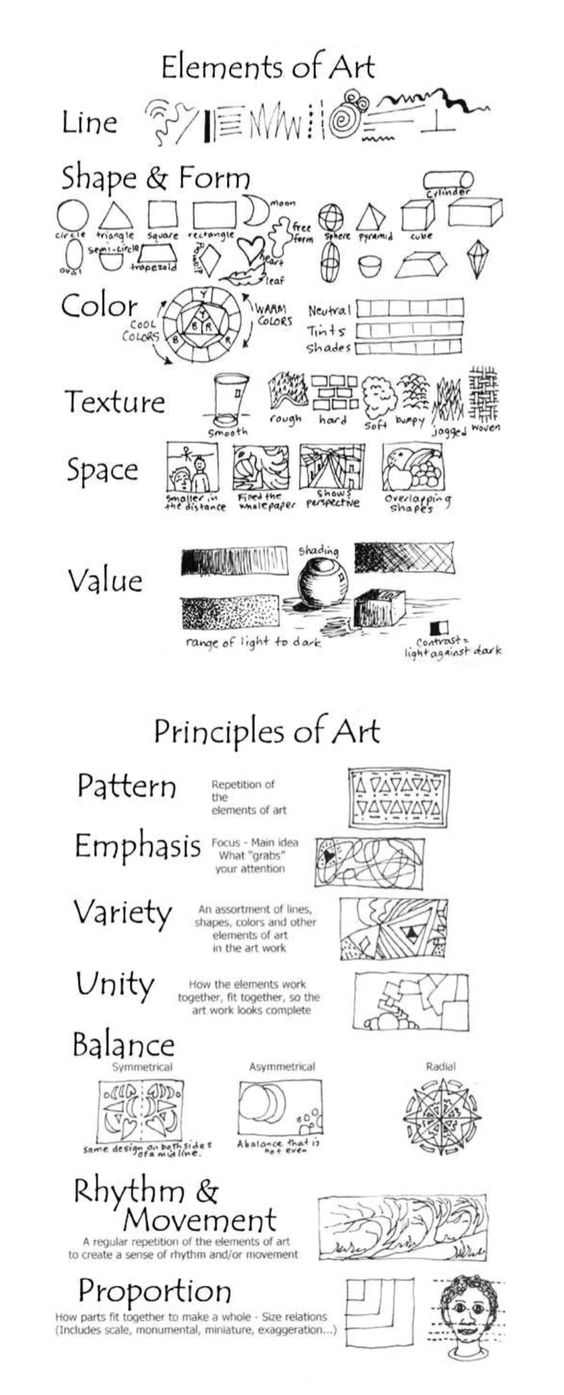
ELEMENT OF ART & TEXTURE